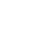News
Topological segregation of stress sensors along the gut crypt–villus axis
The crypt–villus structure of the small intestine serves as an essential protective barrier. The integrity of this barrier is monitored by the complex sensory system of the gut, in which serotonergic enterochromaffin (EC) cells play an important part.
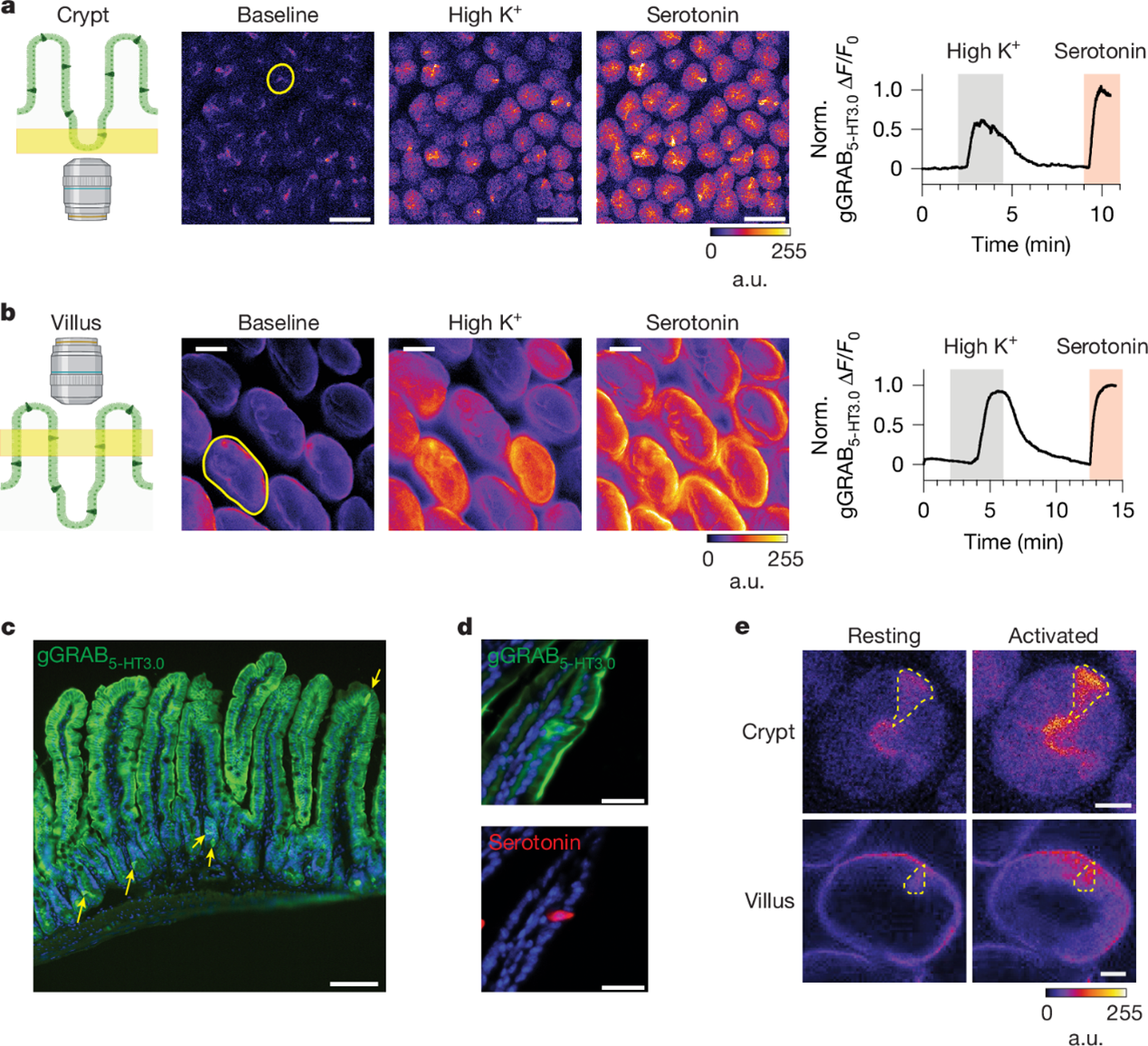
SecY translocon chaperones protein folding during membrane protein insertion
The Sec translocon is vital for guiding membrane protein insertion into lipid bilayers. The insertion and folding processes of membrane proteins are poorly understood.
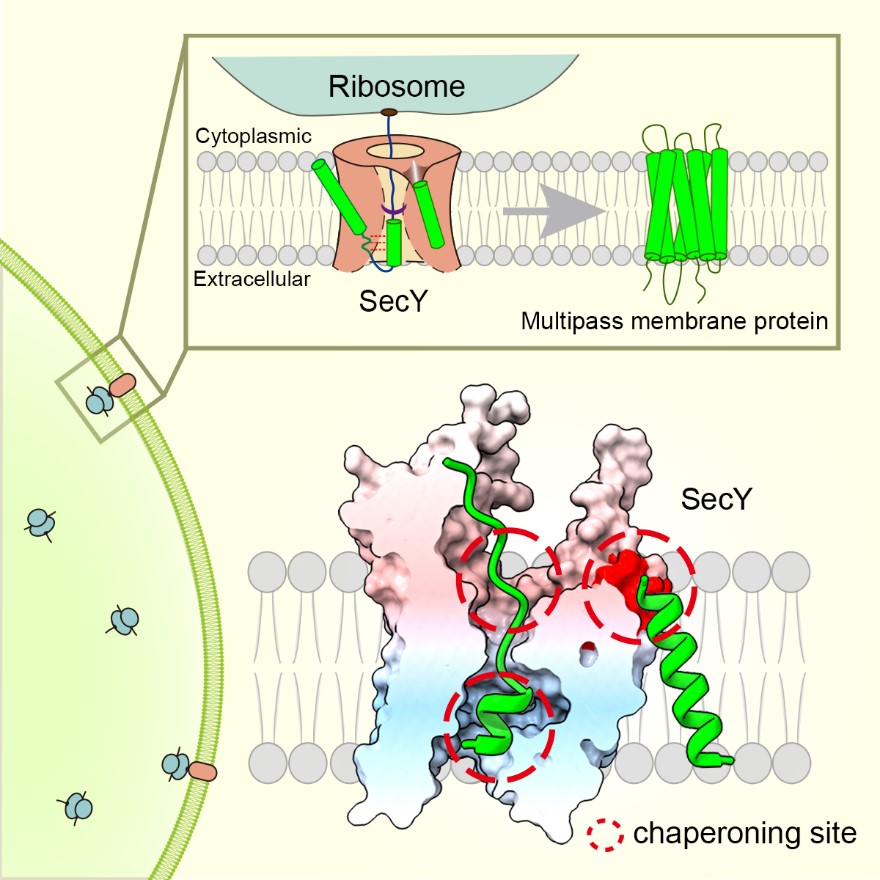
Molecular glue for phycobilisome attachment to photosystem II in Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002
Phycobilisomes (PBS) are the major photosynthetic light-harvesting complexes in cyanobacteria and red algae. While the structures of PBS have been determined in atomic resolutions, how PBS are attached to the reaction centers of photosystems remains less clear. Here, we report that a linker protein (LcpA) is required for the attachment of PBS to photosystem II (PSII) in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp.
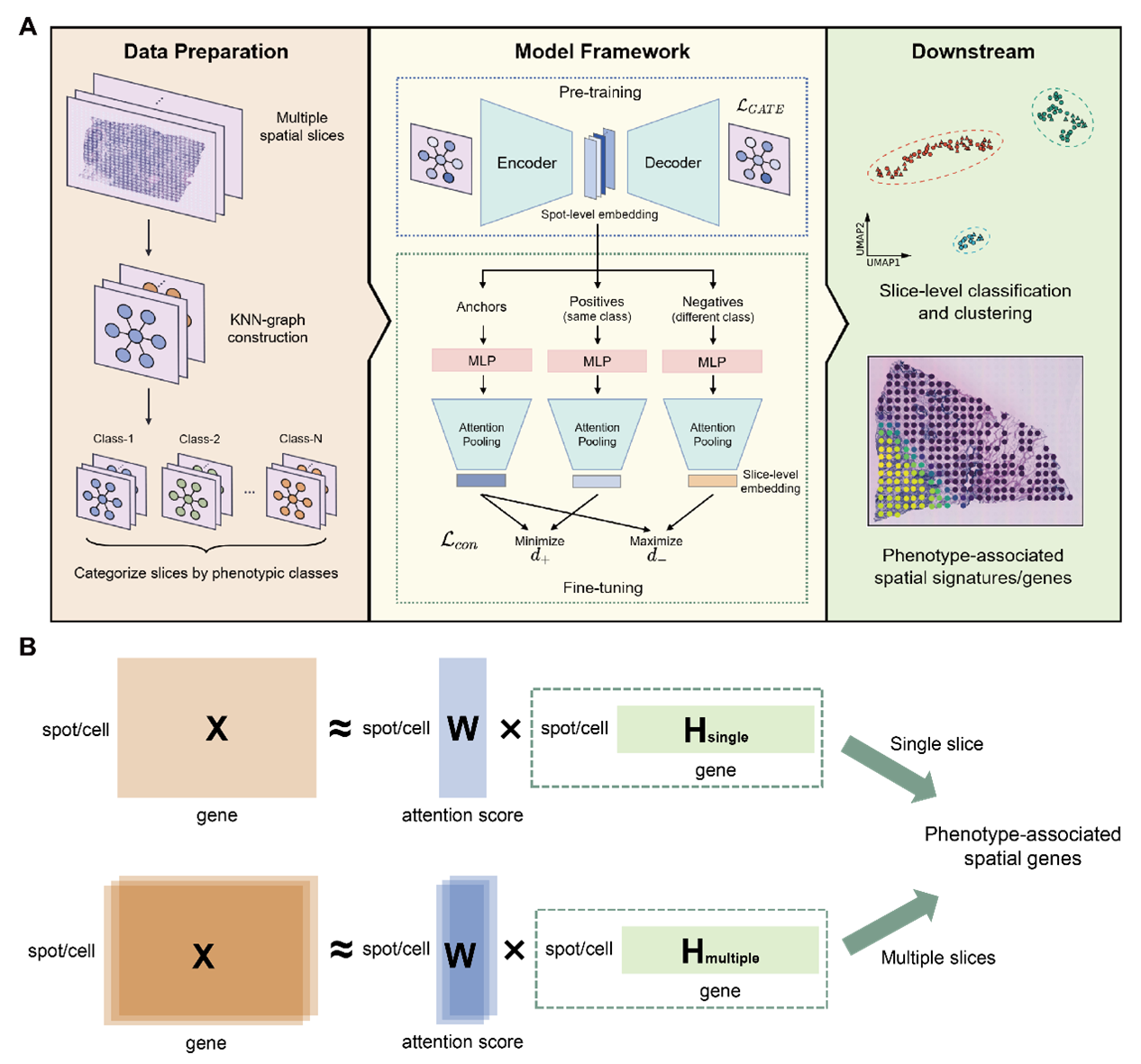
Learning Phenotype Associated Signature in Spatial Transcriptomics with PASSAGE
Spatially resolved transcriptomics (SRT) is poised to advance the understanding of cellular organization within complex tissues under various physiological and pathological conditions at unprecedented resolution.
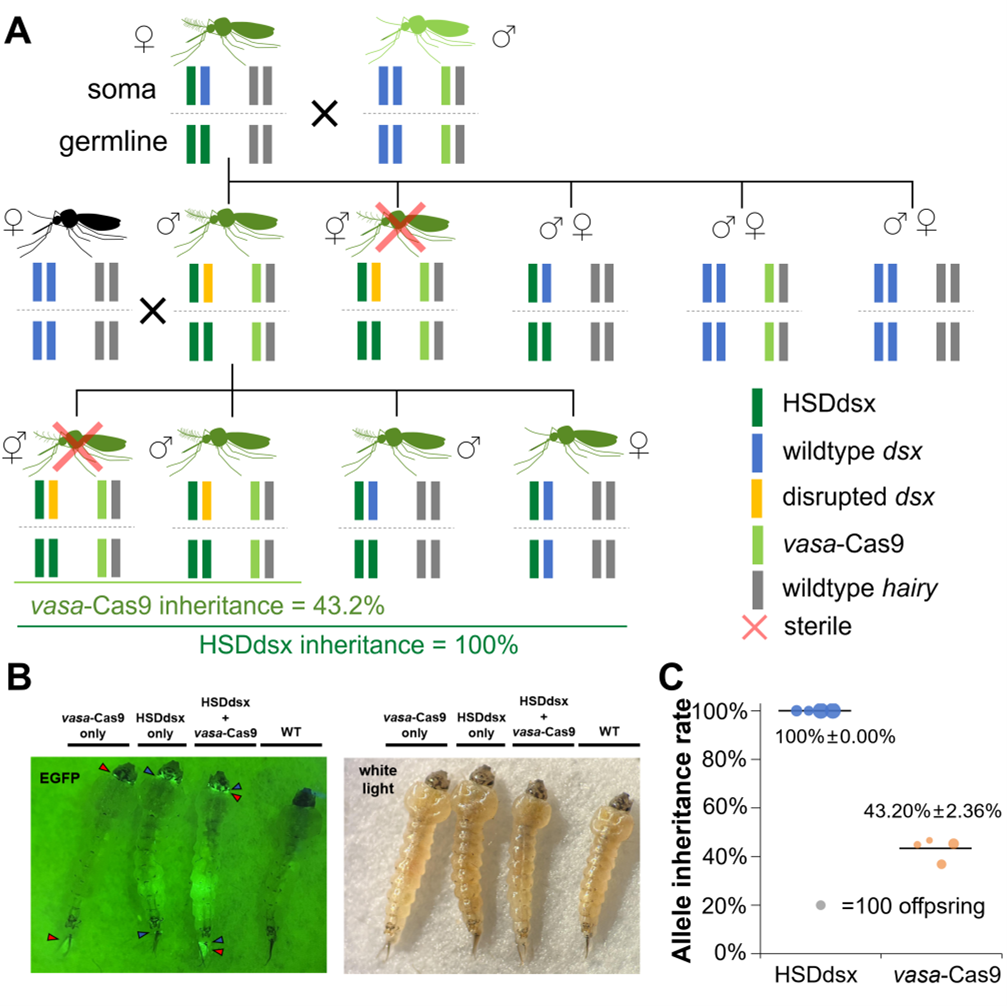
Gene drive-based population suppression in the malaria vector Anopheles stephensi
Gene drives are alleles that can bias the inheritance of specific traits in target populations for the purpose of modification or suppression. Here, we construct a homing suppression drive in the major urban malaria vector Anopheles stephensi targeting the female-specific exon of doublesex

Topological segregation of stress sensors along the gut crypt–villus axis
The crypt–villus structure of the small intestine serves as an essential protective barrier. The integrity of this barrier is monitored by the complex sensory system of the gut, in which serotonergic enterochromaffin (EC) cells play an important part.

SecY translocon chaperones protein folding during membrane protein insertion
The Sec translocon is vital for guiding membrane protein insertion into lipid bilayers. The insertion and folding processes of membrane proteins are poorly understood.